Spells Creation Demonstration Guide
The R script calculate_spells.R converts point in time data to spells.
Dependencies
Running this code requiers the following libraries:
-
dplyr -
data.table -
doParallel
Follow the instructions in the tutorials section to install these libraries.
Description of Files
The R File
The calculate_spells.R file is the code file written in R to
transform monthly extracts of case information into a spells format more
suited for longitudinal analysis. A spell represents a period of time
when the characteristics of a case remain the same. At a minimum, a
spell can be defined as the period for when a case is active, but other
case characteristics may be optionally considered, such as if a case
changes case type or the size of the household changes.
Input File
For the demonstration, we provide an input file of mock monthly extracts called input.csv (in the test_data directory). It has the following basic format which should match the format of the file you are preparing for analysis:
| caseid | date | benefits | case_type | num_adults |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1/1/2016 | 1 | child only | 0 |
| 1 | 2/1/2016 | 1 | child only | 0 |
| 1 | 3/1/2016 | 1 | child only | 0 |
| 1 | 4/1/2016 | 1 | one parent | 1 |
| 1 | 5/1/2016 | 1 | one parent | 1 |
| 1 | 6/1/2016 | 1 | one parent | 1 |
| 1 | 7/1/2016 | 0 | one parent | 1 |
| 1 | 8/1/2016 | 0 | one parent | 1 |
| 1 | 9/1/2016 | 0 | one parent | 1 |
| 1 | 10/1/2016 | 0 | one parent | 1 |
| 1 | 11/1/2016 | 0 | one parent | 1 |
| 1 | 12/1/2016 | 0 | one parent | 1 |
Fields include unique case id, the date of the extract time period (usually one record per month), and a flag indicating if the case was receiving benefits for that time period (1 for receiving or 0 for not receiving). These fields should be labeled: “caseid”, “date”, and “benefits” respectively. Optionally, there can be additional fields that are used to define spells. The example above, and the sample input file, are examples of TANF data with two additional fields, case_type and num_adults. The first additional field, case_type, defines the type of the TANF case, child only, one parent or two parent. The second additonal field, num_adults, is the number of adults on a case. The section on customizing code below explains how to work with additional fields for defining spells. The field names are not case sensitive, so they may be capitalized or lower case. All fields can be either numeric or character. Explicitly recording inactive cases in the monthly extract input file is optional, as missing months will be inferred as inactive and used to calculate
Output File
The output file is created once the R file is run with the input file. It contains the spells created by the code. Additional fields such as “case_type” or “num_adults” will be added to the output file if they are added to the CASE_FIELDS code parameter. For details on the CASE_FIELDS code parameter, see the “Customizing the Code for Your Data” section of this guide. The output file will have this structure:
| caseid | benefits | startMonth | endMonth | spellLength |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 01/2016 | 06/2016 | 6 |
| 1 | 0 | 07/2016 | 12/2016 | 6 |
The spells above refers to the monthly records in the input file above.
Summary File
The summary file is created once the R file is run with the input file. It contains summary information on the spells such as the number of spells and the average length of the spells for active and inactive cases.
How to Run the Code
Before running the code, you will need to install the programs listed in the Installation Guide document. Open the R file “calculate_spells.R” in Rstudio. There are a few code parameters that you will need to change before the code can run.
-
INPUT_FILE (character): This code parameter stores the filepath where your input file containing case information is stored. It must be a .csv file type.
-
OUTPUT_FILE (character): This code parameter stores the filepath where you want the spells to be saved once calculated. It must be a .csv file type.
-
SUMMARY_FILE (character): This code parameter stores the filepath where you want the summary file to be saved once statistics on the spells are available. It must be a .txt file type.
NOTE: Windows users will need to format your filepaths differently in R. A Windows filepath looks like “C:/Folder1/Subfolder/MyFile.csv”. In R, the filepath would need to look like “C://Folder1//Subfolder//MyFile.csv”.
Changing those 3 code parameters, is enough to run the code with its default code parameters for CHURN and CASE_FIELDS. However, you may wish to change these two code parameters depending on your specific data. This is described in the next section.
Customizing the Code for Your Data
There are two optional code parameters you can change in the code depending on your needs:
-
CHURN (integer): The CHURN code parameter allows states to define how long (in months) to wait for a case to be inactive before considering it closed and creating a new spell. Your state may wish to customize the length of a service gap to ignore as administrative churn when defining spells. Administrative churn refers to a short temporary stop in service for administrative reasons rather than a longer term change in case eligibility. The default length is 0 months meaning any service gap is considered a new spell. Setting it to 1 means ignore service gaps of 1 month or shorter when creating spells. Setting to 2 means ignore all service gaps 2 months or shorter when creating spells, etc.
-
CASE_FIELDS (character vector): The CASE_FIELDS code parameter allows states to add additional fields other than benefits status to detect changes in when defining spells. States may wish for spells to be based on other case characteristics in addition to whether the case is receiving benefits. For example, an agency may wish to create spells if a case stops receiving benefits, if the case changes case type, or if the number of adults in the household changes. Add the field names representing these fields in your input file to the CASE_FIELDS code parameter. For example, the CASE_FIELDS code parameter may look like this
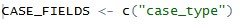
Examples of How to Run the Code
The sample input file provided for this demonstration contains 3 unique cases with two years of case history. The number of spells created in the output file depend on how the agency wishes to define spells. There are two code parameters within the “calculate_spells.R” file that can change the number of spells outputted: the CHURN code parameter and the CASE_FIELDS code parameter.
-
Save the “calculate_spells.R” and the “input.csv” files provided in this tutorial somewhere accessible to where you have installed R.
-
Change the INPUT_FILE and OUPUT_FILE code parameters to the filepaths where you have saved the files in step 1. Set the SUMMARY_FILE code parameter to the filepath where you want the summary file to be saved. Your code may look like this:

Notice how the folders are separated by two backslashes instead of one backslash. That is how R reads Window’s filepaths. If you are working on a Mac or Linux operating system you need to use a forward slash instead of the double backslashes. For more information on R filepaths see this explanation from Indiana University.
-
Run the code in RStudio. From the top navigation bar select Code > Run Region > Run All.
-
Examine the output file. The code ran with the default values for the code parameters CHURN and CASE_FIELDS. Any gap in benefits receipt will be considered a new spell, and the code will only look at the “benefits” column when doing change detection for spells. Your output file should match below. Caseid 1 has 12 spells. If you look at the input.csv file for caseid 1, you will notice that it starts active and changes status every 2 months for 2 years.
caseid benefits startMonth endMonth spellLength 1 1 01/2016 02/2016 2 1 0 03/2016 04/2016 2 1 1 05/2016 06/2016 2 1 0 07/2016 08/2016 2 1 1 09/2016 10/2016 2 1 0 11/2016 12/2016 2 1 1 01/2017 02/2017 2 1 0 03/2017 04/2017 2 1 1 05/2017 06/2017 2 1 0 07/2017 08/2017 2 1 1 09/2017 10/2017 2 1 0 11/2017 12/2017 2 2 1 01/2016 12/2017 24 3 1 01/2016 12/2017 24 -
Examine the summary file. It should say there are 8 active spells and 6 inactive spells as well as some other descriptive statistics about the spells. This matches the output file results.
Changing the CHURN Code Parameter
-
In the R code, change the CHURN code parameter value from 0 to 2. If the CHURN code parameter is less than 2, caseid 1 will have 12 distinct spells. If we changed the CHURN code parameter to 1, the code would ignore 1 month service gaps when creating spells. In this example, that will not affect the output since all of the gaps are 2 months.
-
Save the changes to your R code (Ctrl + S or the Save button in RStudio). Rerun the code as we did previously.
-
Examine the output file. Caseid 1 now has significantly fewer spells. The short two month service gaps were assumed to be administrative churn and were joined to the active spell for caseid 1. Notice that the last two months remain an inactive spell even though they too represent a 2 month gap. Because the last months of the study period for this case are inactive, it is assumed the case will remain inactive beyond the study period, and therefore the inactive spell remains.
caseid benefits startMonth endMonth spellLength 1 1 01/2016 10/2017 22 1 0 11/2017 12/2017 2 2 1 01/2016 12/2017 24 3 1 01/2016 12/2017 24 -
Examine the summary file. It should say there are 3 active spells and 1 inactive spells as well as some other descriptive statistics about the spells. This matches the output file results.
Tracking Case Type with the CASE_FIELDS Code Parameter
-
In the R code, change the CASE_FIELDS code parameter to look like this.
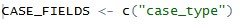
-
Save the changes to your R code (Ctrl + S or the Save button in RStudio). Rerun the code as we did previously.
-
Examine the output file. Notice that the field
case_typewhich was not previously in the output file is now included because we have included it in the CASE_FIELDS code parameter. Caseid 2 starts as a “child only” case_type and changes every 2 months creating a total of 12 spells for caseid 2 which previously only had 1 spell. The output for caseid 2 should now look like this:caseid benefits case_type startMonth endMonth spellLength 2 1 child only 01/2016 02/2016 2 2 1 one parent 03/2016 04/2016 2 2 1 child only 05/2016 06/2016 2 2 1 one parent 07/2016 08/2016 2 2 1 child only 09/2016 10/2016 2 2 1 one parent 11/2016 12/2016 2 2 1 child only 01/2017 02/2017 2 2 1 one parent 03/2017 04/2017 2 2 1 child only 05/2017 06/2017 2 2 1 one parent 07/2017 08/2017 2 2 1 child only 09/2017 10/2017 2 2 1 one parent 11/2017 12/2017 2 -
Examine the summary file. Its results will be different than before. Its exact results will vary depending on how you have the CHURN code parameter set now.
Tracking Case Type and Number of Adults with the CASE_FIELDS Code Parameter
-
In the R code, change the CASE_FIELDS code parameter to look like this.

Now the code looks for changes in either field when creating spells.
-
Save the changes to your R code (Ctrl + S or the Save button
-
Examine the output file. The field
num_adultsis now included in the output file in addition tocase_typebecause we have included it in the CASE_FIELDS code parameter. Caseid 3 changesnum_adultsevery 2 months creating 12 total spells. The output for caseid 3 should now look like this:caseid benefits case_type num_adults startMonth endMonth spellLength 3 1 one parent 1 01/2016 02/2016 2 3 1 two parent 2 03/2016 04/2016 2 3 1 one parent 1 05/2016 06/2016 2 3 1 two parent 2 07/2016 08/2016 2 3 1 one parent 1 09/2016 10/2016 2 3 1 two parent 2 11/2016 12/2016 2 3 1 one parent 1 01/2017 02/2017 2 3 1 two parent 2 03/2017 04/2017 2 3 1 one parent 1 05/2017 06/2017 2 3 1 two parent 2 07/2017 08/2017 2 3 1 one parent 1 09/2017 10/2017 2 3 1 two parent 2 11/2017 12/2017 2 -
Examine the summary file. Its results will be different than before. Its exact results will vary depending on how you have the CHURN code parameter set now.
There are 3 caseids included in the sample input for 2 years of case
history. Using the examples presented here, the amount of spells
outputted can range from 4 spells to 36 spells depending on how you set
the code parameters within the calculate_spells.R code.